Understanding Micron Technology Inc (NAS:MU)
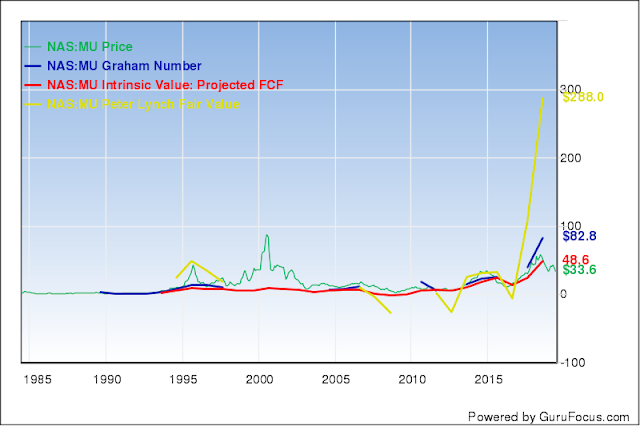
The first thing you'll notice is that Micron is undervalued mostly however you see it. Is hard to ignore that P/E of 3.12, in theory you should get your money back ever 3 years, and that for every dollar of their 30 billion in sales, they keep 50 cents (operating margins of almost 50%).
But just before you run and buy Micron, take a look.

Micron is a very cyclical market. It goes up and down like a yoyo. that makes it hard to value, specially because its net income is even more chaotic:

Here is the problem, expectations are that revenues are about to fall... a lot, because of prices of their products are:
As a reference last time revenues lower significantly was in 2016, they operated at a loss that year. stock price low was around $10
Is debt a problem? actually no.
Micron Technology Inc Annual Data
A high Debt-to-EBITDA ratio generally means that a company may spend more time to paying off its debt.
According to Joel Tillinghast's BIG MONEY THINKS SMALL: Biases, Blind Spots, and Smarter Investing , a ratio of Debt-to-EBITDA exceeding four is usually considered scary unless tangible assets cover the debt.
CEO Sanjay Mehrotra argues that fundamental trends are strong. And I agree, in the long term. Autonomous vehicles for example (5 to 10 years away maybe? who knows) will have more than a Terabyte of storage inside, and more than a hundred gigabyte of DRAM inside de car. That's like a datacenter in each car. By the way, Micron is, today, market share leader in the automotive market.
Micron is a 40 year old company, the most comprehensive portfolio of technologies for memory and storage
Innovation capabilities
four business units (which are also our reportable segments) in various forms, including wafers, components, modules, SSDs and in MCPs that combine DRAM, NAND, and/or NOR with a controller and firmware
5G developments will need more memory as well and artificial intelligence
3 biggest player after Samsung, SK Hynix. They represent 90% of revenue in the industry
Other players to take on account are nanya, winbond, and Powerchip.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dZcszUj5szA
3D NAND
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FWV5z9qTUK8
Description of Memory and Storage Products
four business units (which are also our reportable segments) in various forms, including wafers, components, modules, SSDs and in MCPs that combine DRAM, NAND, and/or NOR with a controller and firmware
5G developments will need more memory as well and artificial intelligence
3 biggest player after Samsung, SK Hynix. They represent 90% of revenue in the industry
Other players to take on account are nanya, winbond, and Powerchip.
NAND AND DRAM PROJECTIONS:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dZcszUj5szA
3D NAND
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FWV5z9qTUK8
Product Descriptions
|
Description of Memory and Storage Products
DRAM
DRAM products are high-density, low-cost-per-bit, random access memory devices that provide high-speed data storage and retrieval with a variety of performance, pricing, and other characteristics.
Wafer, Component, and Module DRAM: DDR3 and DDR4 DRAM products offer high speed and bandwidth, primarily for use in computers, servers, networking devices, communications equipment, consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications.
LPDRAM: LPDRAM products offer lower power consumption relative to other DRAM products and are used primarily in smartphones, tablets, automotive applications, laptop computers, and other mobile consumer devices that require low power consumption.
NAND
NAND products are electrically rewritable, non-volatile semiconductor memory and storage devices that retain content when power is turned off. NAND is ideal for mass-storage devices due to its fast erase and write times, high density, and low cost per bit relative to other solid-state memories. NAND-based storage devices are utilized in smartphones, SSDs, tablets, computers, automotive and industrial applications, networking, and other consumer applications. Removable storage devices, such as USB and Flash memory cards, are used with applications such as PCs, digital still cameras, and smartphones. The market for NAND products has grown rapidly and we expect it to continue to grow due to increased demand for these and other embedded and removable storage devices.
Wafer and Component NAND : Our NAND products feature a small cell structure that enables higher densities for demanding applications. 3D NAND stacks layers of data storage cells vertically to create storage devices with higher capacity than competing planar NAND technologies. This enables more storage in a smaller space, bringing significant cost savings, low power usage and high performance to a range of mobile consumer devices as well as the most demanding enterprise deployments.
SSDs: SSDs incorporate NAND, a controller, and firmware and are a significant portion of our net sales. We offer client, cloud, and enterprise SSDs which feature higher performance, reduced-power consumption, and enhanced reliability as compared to typical hard disk drives.
MCPs and Managed NAND: We offer MCP products that combine DRAM, NAND, and/or NOR with a controller and firmware. Our managed NAND includes eMMC and universal flash storage solutions, which each combine high-capacity NAND with a high-speed controller and firmware in a small ball-grid array, and eMCP products, which combine an eMMC/UFS solution with LPDRAM.
NOR Flash
NOR Flash products are electrically re-writeable semiconductor memory devices that offer fast read times and are used in automotive, industrial, connected home, and consumer applications.
3D XPoint Memory
We introduced 3D XPoint technology, a new category of non-volatile memory, in 2015. 3D XPoint memory's innovative, transistor-less, cross point architecture creates a three-dimensional checkerboard where memory cells sit at the intersection of word lines and bit lines, allowing the cells to be addressed individually. As a result, data can be written and read in small sizes, leading to fast and efficient read/write processes. We began producing 3D XPoint memory in 2016.
Compute and Networking Business Unit
CNBU includes memory products and solutions sold into cloud server, enterprise, client, graphics, and networking markets. CNBU reported revenue of $15.25 billion in 2018
Cloud Server: The cloud server market was CNBU's fastest growing market in 2018, particularly in datacenters, with significant increases in DRAM content per server. The cloud server market has been driven, in part, by intelligent edge devices capable of artificial intelligence and augmented reality that store and access data in the cloud. Artificial intelligence servers require significantly increasing quantities of DRAM and as the number and capabilities of these intelligent edge devices increase, more data is stored, processed, and accessed in the cloud, creating a virtuous cycle between the cloud and edge devices. We anticipate continued growth of our 1Xnm portfolio with the continued ramp of our second-generation 1Xnm 8Gb DDR4 products, which were validated with key partners and customers in 2018.
Storage Business Unit
Embedded Business Unit
Semiconductor manufacturing is extremely capital intensive, requiring large investments in sophisticated facilities and equipment
"According to interviews with the hedge fund manager, the main reason Tepper likes Micron is that he believes that the demand for microchips will remain healthy over the long term, supported by growth in demand for connected devices and cloud computing. He's also bullish on the company's management team after it announced a $10 billion stock buy-back commitment in the middle of last year and announced the company would be returning 50% of free cash flow to shareholders beginning in fiscal 2019.